Abundance: uncommon
What: root/tuber
How: roasted
Where: open fields, landscaping
When: fall, winter
Nutritional Value: calories
Edible gayfeather tuber.

Young gayfeather plant (early June in Houston).

A stand of gayfeather plants.

Close-up of gayfeather stand.

Close-up of gayfeather flower.

Close-up of gayfeather flower before opening.

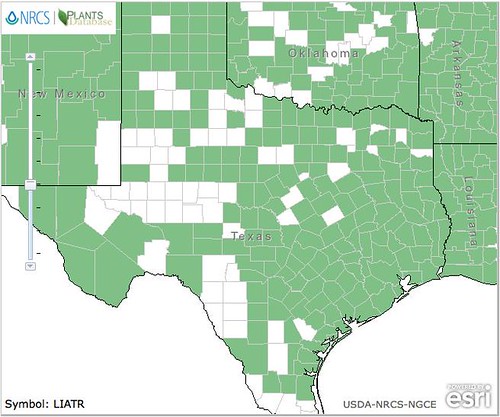
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
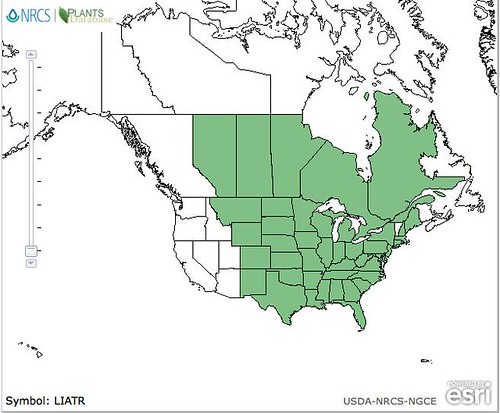
There are quite a few different species of Gayfeathers growing in stands across the fields, prairies, ditches, and woodland glades of Texas and North America. All are considered non-poisonous but only a few of them produce tubers big enough to be worth eating. Their tall, unbranching spikes start green, then erupt with many small, purple flowers, followed by browning as they dry. During the winter months clusters of these old stalks are easy spot, even through snow on the central plains. The drought-resistant Liatris spica are becoming popular in low-water xeriscapes and can often be found at big-box home improvement stores.
Gayfeather tubers continue to grow larger year after year but only the latest-year's portion is tender enough to eat, with the common species Liatris spica being considered the best. Memorize the location of the summer-blooming purple flower stalks for harvesting the tubers in the fall and winter. Once harvested, use these tubers as you would potatoes. They do well boiled or roasted.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

